- Doctors & Departments
-
Conditions & Advice
- Overview
- Conditions and Symptoms
- Symptom Checker
- Parent Resources
- The Connection Journey
- Calm A Crying Baby
- Sports Articles
- Dosage Tables
- Baby Guide
-
Your Visit
- Overview
- Prepare for Your Visit
- Your Overnight Stay
- Send a Cheer Card
- Family and Patient Resources
- Patient Cost Estimate
- Insurance and Financial Resources
- Online Bill Pay
- Medical Records
- Policies and Procedures
- We Ask Because We Care
Click to find the locations nearest youFind locations by region
See all locations -
Community
- Overview
- Addressing the Youth Mental Health Crisis
- Calendar of Events
- Child Health Advocacy
- Community Health
- Community Partners
- Corporate Relations
- Global Health
- Patient Advocacy
- Patient Stories
- Pediatric Affiliations
- Support Children’s Colorado
- Specialty Outreach Clinics
Your Support Matters
Upcoming Events
Public Meeting: 2024 Community Benefit and Hospital Transformation Program
Tuesday, May 14, 2024Join Children's Hospital Colorado at one of our virtual events to learn...
-
Research & Innovation
- Overview
- Pediatric Clinical Trials
- Q: Pediatric Health Advances
- Discoveries and Milestones
- Training and Internships
- Academic Affiliation
- Investigator Resources
- Funding Opportunities
- Center For Innovation
- Support Our Research
- Research Areas

It starts with a Q:
For the latest cutting-edge research, innovative collaborations and remarkable discoveries in child health, read stories from across all our areas of study in Q: Advances and Answers in Pediatric Health.


Common Neurological Tests
We provide comprehensive care for developmental and nervous system disorders ranging from complex neurosurgery to cognitive and behavioral counseling.

Doctors at the Neuroscience Institute at Children’s Hospital Colorado use various tests to diagnose possible neurological conditions in babies, kids and young adults. These tests are also often used on an ongoing basis in your child’s follow-up care. Our neurosciences team provides excellent care within a state-of-the-art facility to perform and interpret neurological functioning tests.
What tests might my child have?
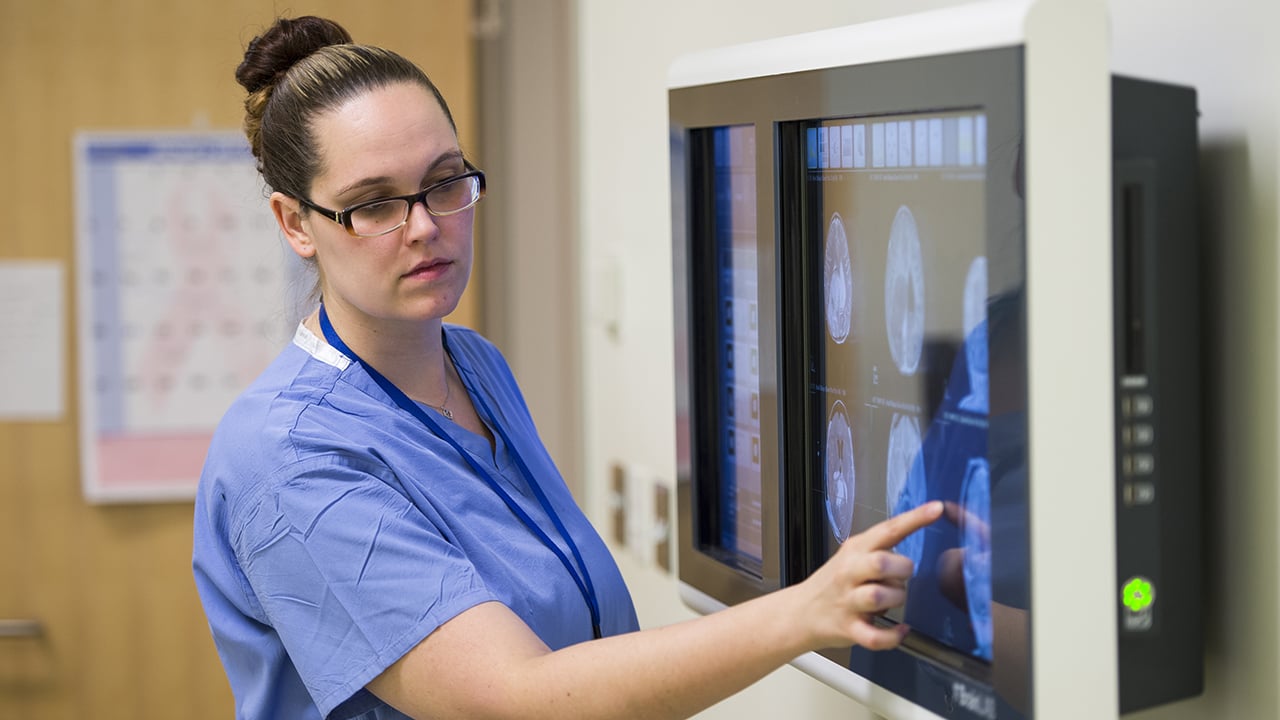
If your child is a patient at the Neuroscience Institute, he or she will probably experience one or more tests. As a parent, it’s important for you to know that our doctors, nurses and technicians are specially trained to perform and explain these procedures to your child and help him feel calm during a test.
We also have special testing equipment designed to fit the various sizes and ages of children, which helps our testing to be as accurate and comfortable as possible. Read more about neurodiagnostic testing.
Types of neurological diagnostic tests
Electromyography (EMG)
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that assesses the health of the muscles and the nerves controlling the muscles. In an EMG, a needle electrode is inserted through the skin into the muscle. The electrical activity detected by the electrode is displayed on an oscilloscope and may be heard through a speaker. After placement of the electrodes, your child may be asked to contract the muscle (for example, by bending the arm). The wave form produced on the oscilloscope provides information about the ability of the muscle to respond when the nerves are stimulated. EMG testing helps to differentiate primary muscle conditions from muscle weakness caused by neurological disorders.
Nerve conduction velocity test
A nerve conduction velocity test is usually performed in conjunction with an EMG. This test evaluates the speed of conduction of impulses through a nerve. The nerve is stimulated, usually with electrodes that are placed on the skin. One electrode stimulates the nerve with a very mild electrical impulse. The resulting electrical activity is recorded by the other electrodes. The distance between electrodes and the time it takes for electrical impulses to travel between electrodes are used to calculate the nerve conduction velocity. This test is used to diagnose nerve damage or destruction. Abnormal results can indicate peripheral neuropathy, damage to the spinal cord and other conditions.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test to detect abnormalities in the electrical activity of the brain. Brain cells communicate by producing tiny electrical impulses. In an EEG, electrodes are placed on the scalp over multiple areas of the brain to detect and record patterns of electrical activity and check for abnormalities. An EEG test is used to help diagnose the presence and type of seizure disorders, as well as help in the diagnosis of other disorders. Inpatient video-EEG monitoring is used to localize seizure onset in patients undergoing evaluation for epilepsy surgery. It is also used to confirm an epilepsy diagnosis.
Evoked potential tests
Evoked potential tests measure the transmission of electrical signals within the brain and spinal cord. It is used to diagnose multiple sclerosis (MS) and other conditions.
Lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture is a procedure used to measure the pressure inside the head (intracranial pressure) or to remove a small amount of the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord (cerebrospinal fluid) for laboratory testing. During a lumbar puncture, a small hollow needle is inserted in the space between the lumbar (low back) vertebrae below the level of the spinal cord, and fluid is removed or pressure measurements are taken. Lumbar puncture testing helps to determine if headaches or vision concerns are related to increased pressure or to test for causes of developmental problems, seizures, degenerative disease, infections, or metabolic problems that affect the brain.
Sleep tests
A sleep study (also called a polysomnogram) is a test that records your child’s physical state during various stages of sleep and wakefulness. It provides data that are essential in evaluating sleep and sleep-related complaints, such as identifying sleep stages, body position, blood oxygen levels, respiratory events, muscle tone, heart rate and general sleep behavior. This information may be used to help diagnose causes of headaches, restless leg syndrome, muscle weakness, or fatigue. Learn more about our Sleep Center.
Radiology tests
Radiology tests (also known as imaging tests) are studies that produce pictures of what’s going on inside the body. These tests use different forms of energy (X-rays, sound waves, radioactive particles, or magnetic fields) that are passed through the body and converted into images on a machine. These images can show normal body structure and function as well as abnormalities caused by diseases.
Laboratory tests
Children's Colorado provides leading-edge laboratory and pathology services for pediatric patients in the state of Colorado and the Rocky Mountain region. In addition to the routine procedures available 24 hours a day, the laboratory offers many specialized tests designed for unique pediatric diseases. All tests are done by qualified and certified staff, and are reviewed by a multidisciplinary team of physicians who will explain the results to your family and child.
Genetic tests
Genetic tests can often resolve uncertainty about genetic risks and confirm a diagnosis. For most patients, testing involves taking only a blood sample. A few tests involve taking hair, skin or other tissue samples. Learn more about why genetic testing is used.
See a list of conditions we treat.
Contact Us
Phone: 720-777-4513
Fax: 720-777-7201



 720-777-0123
720-777-0123



